Supermassive black holes and Active Galactic Nuclei
Cosmic evolution of supermassive black holes
Co-moving space density of X-ray selected Active Galactic Nuclei
Silverman, J. D., Green, P. J., Barkhouse, W. et al. 2005, ApJ, 624, 630
The luminosity function of X-ray selected Active Galactic Nuclei: Evolution of Supermassive Black Holes at high redshift
Silverman, J., Green, P.J. et al. 2008, ApJ, 679, 118
The cosmic growth of the active black hole population at 1 < z < 2 in zCOSMOS, VVDS and SDSS
Schulze, A., Bongiorno, A., Gavignaud, I., Schramm, M., Silverman, J. et al. MNRAS, 447, 2085
AGN and star formation relation
The Evolution of AGN Host Galaxies: From Blue to Red and the Influence of Large-Scale Structures
Silverman, J., Mainieri, V., Lehmer, B. et al. 2008, ApJ, 675, 1025
Ongoing and Co-evolving Star Formation in zCOSMOS galaxies hosting Active Galactic Nuclei
Silverman, J. D., Lamareille, F., Maier, C., Lilly, S. et al. 2009, ApJ, 696, 396
The mean star-forming properties of QSO host galaxies
Rosario, D., Trakhtenbrot, B., Lutz, D. et al. 2014, A&A, 560, 72
Role of mergers and interactions
The Impact of Galaxy Interactions on Active Galactic Nucleus Activity in zCOSMOS
Silverman, J.D., Kampczyk, P., Jahnke, K., Andrea, R., et al. 2011, ApJ, 743,2
Late-stage mergers in COSMOS to z ~ 1
Lackner, C., Silverman, J. et al. 2014, AJ, 148, 137
Environments
The Environments of Active Galactic Nuclei within the zCOSMOS Density Field
Silverman, J. D., Kovac, K., Knobel, C., Lilly, S. et al. 2009, ApJ, 695, 171
The X-ray Zurich Environmental Study (X-ZENS). I. Chandra and XMM-Newton observations of AGNs in galaxies in nearby groups
Silverman, J.D., Miniati, F., Finoguenov, A. et al. 2014, ApJ, 780, 67
Changing ionization conditions in SDSS galaxies with AGN as a function of environment from pairs to clusters
Khabiboulline, E., Steinhardt, C., Silverman, J. D. et al. 2014, ApJ, 795, 62
Black hole mass - galaxy mass relations
The Black Hole-Bulge Mass Relation of Active Galactic Nuclei in the Extended Chandra Deep Field-South Survey
Schramm, M. & Silverman, J.D. 2013, ApJ, 767, 13
Accretion disk - corona connection
A statistical relation between the X-ray spectral index and Eddington ratio of active galactic nuclei in deep surveys
Brightman, M., Silverman, J., Mainieri, V., Ueda, Y., Schramm, M. et al. 2013, MNRAS, 433,2485
Discovery of the Most-Distant Double-Peaked Emitter at z=1.369
Luo, B., Brandt, W. N., Silverman, J. D., Strateva, I. V. et al. 2007, ApJ, 695, 1227
Obscured accretion
Hard X-ray emitting Active Galactic Nuclei selected by the Chandra Multi-wavelength Project
Silverman, J., Green, P., Barkhouse, W., Kim, D.-W. et al. 2005, ApJ, 618, 123
Broad emission-line region
A Comparative Analysis of Virial Black Hole Mass Estimates of
Moderate-luminosity Active Galactic Nuclei Using Subaru/FMOS
Matsuoka, K., Silverman, J.D., Schramm, M. et al. 2013, ApJ, 771, 64
Quasars with Anomalous Hβ profiles. I. Demographics
Steinhardt, C., Silverman, J. 2013, PASJ, 65, 4
SDSS 0956+5128: A broad-line quasar with extreme velocity offsets
Steinhardt, C., Schramm, M., Silverman, J.D., et al. 2012, ApJ, 759, 24
Narrow emission-line region
First Results from the FMOS-COSMOS Survey on Far-Infrared Selected
Galaxies: Observations of the Strong Nebular Emission Lines and the
Implications for the Evolving BPT Diagram
Kartaltepe, J., Sanders, D., Silverman, J. et al. 2015, ApJL, 806, 35
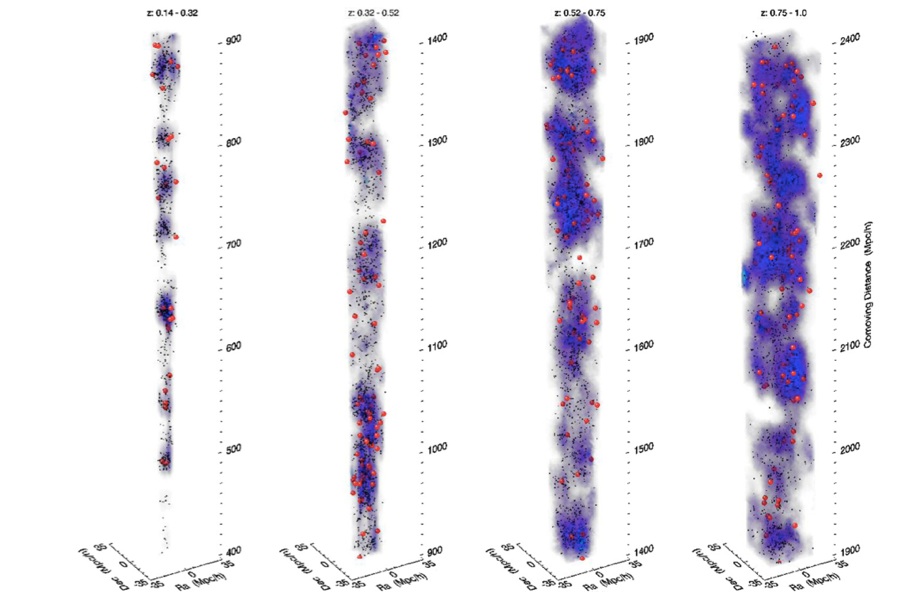
Three-dimensional large-scale distribution of AGN in COSMOS (Silverman et al. 2009) with respect to the zCOSMOS over-density distribution. Each panel shows a different redshift interval as labeled. X-ray-selected AGN are marked in red, while zCOSMOS galaxies that trace large scale filaments are shown by the small black dots.
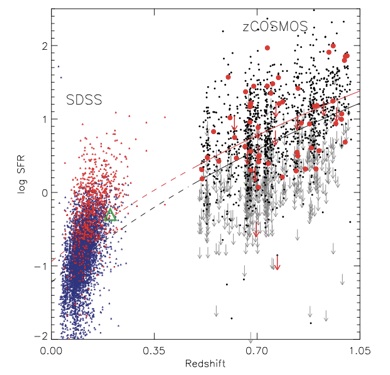
Star formation rate of the host galaxies of X-ray selected AGN in COSMOS survey (Silverman et al. 2009). Star formation rates and spectroscopic redshifts are provided by zCOSMOS, an optical spectroscopic survey using VIMOS on the VLT. Galaxies hosting AGN are identified by their X-ray emission detected by XMM-Newton.
Black holes, over a million times the mass of our Sun, lurk in the center of most massive galaxies. Fundamental questions in astrophysics about their nature are currently unanswered: How are such massive compact objects formed? What physical mechanisms (e.g., galaxy mergers, dynamical instabilities) are conducive to gas inflow to the nuclear region? What processes are driving the global evolution of Active Galactic Nuclei and quasars that mirrors the cosmic star formation rate density?
We are using multi-wavelength observations of deep survey fields to characterize the underlying galaxy population (e.g., stellar mass, star formation rate) and identify those hosting actively accreting black holes, primarily through their X-ray emission less susceptible to obscuration by dust. Our focus has been on disentangling observed influences over a range of scales from local to large-scale environments. Scientific results are listed and organized in various interrelated categories.

X-rays (purple), detected by the Chandra Observatory, from a supermassive black hole being activated in galaxies undergoing a merger as evident from HST imaging and VLT spectroscopy.

