| Program A02 | Investigation of deep inside of nuclei and neutron stars with high energy photons |
|---|---|
| Principal Investigator | NAKAMURA, Satoshi N. (The University of Tokyo) |
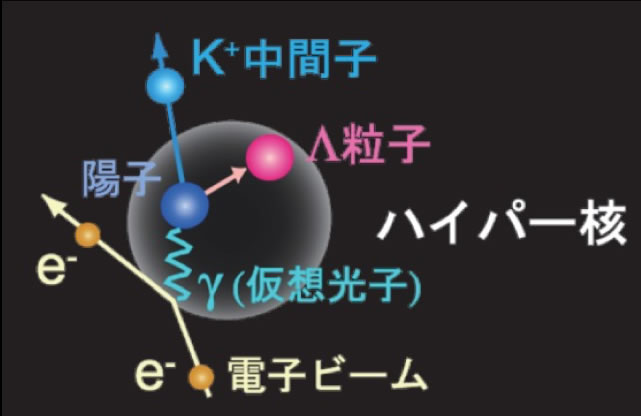
We will perform precise electromagnetic spectroscopy of Λ
hypernuclei using virtual and real photons produced from the high
energy electron beam obtained at Thomas Jefferson National
Accelerator Facility (JLab, USA), Mainz Microtron (MAMI, Germany) and
ELPH-Tohoku Univ. The study will enable us to measure Charge Symmetry
Breaking (CSB) of the Λ ΛN interactions, isospin
dependence of heavy hypernuclei with unprecedented accuracy and
dramatically deepening the knowledge of baryonic force which is
essential to solve the heavy neutron star puzzle (Hyperon
Puzzle).
Particles called hyperons, including strange quarks, can be discussed
in the same frame work (SU(3) symmetry) to protons and neutrons that
make up the usual nuclei, and the hyperon can be a component of a
nucleus. Nuclei including strange quarks are called
"hypernuclei". Hypernuclei do not exist naturally on the earth,
however, the possibility is seriously discussed that hyperons exist
naturally in the center of a compact star called a neutron star,
which is the densest substance in the universe. The neutron star is a
huge single nucleus with a radius of about 10 km and the
gravitational wave was observed from the neutron star merger in
2017. A possibility that elements heavier than iron were made by the
neutron star merger was discussed and neutron star is now a very hot
research subject.
The relation between the mass and size of a neutron star can be
derived from its Equation of State (equation describing its
stiffness), but based on the knowledge of the conventional baryonic
force, the maximum mass of the neutron star including hyperons cannot
exceed about 1.6 times solar mass. This situation is similar that a
huge Tofu (soya cake) is crushed by its own weight and Tofu of the
building size cannot be made. However, in recent years, neutron stars
with twice the solar mass were observed, and neutron stars were found
to be "harder" than we thought. This problem is called "hyperon
puzzle" and it is an extremely important problem to be solved in
nuclear physics. In order to solve this problem, it is essential to
have a deep understanding of the baryonic force in neutron rich and
high density environment, but it is impossible to directly observe
the central part of the neutron star to investigate it. Therefore, we
will proceed experiments to artificially create hypernuclei, which
are miniatures in the center of neutron stars, using virtual photons
at the powerful electron accelerator facilities to investigate its
properties.
Members
| Principal Investigator | NAKAMURA, Satoshi N. (The University of Tokyo) |
 |
|---|---|---|
| Co-Investigator | FUJII, Yuu (Tohoku Medical and Pharmaceutical University) | |
| Research Collaborators | NAGAO, Sho(Tohoku University) | |
| KANETA, Masashi (Tohoku University) | ||
| GOGAMI, Toshiyuki (Kyoto University) | ||
| ISHIKAWA, Takatsugu(Tohoku University) | ||
| HIYAMA, Emiko(Tohoku University & RIKEN) | ||
| AZUMA, Toshiyuki (RIKEN) | ||
| KINO, Yasushi (Tohoku University) | ||
| NOMACHI, Masaharu (Osaka University) |
Reference Materials
- T. Gogami et al., “Experimental techniques and performance of Λ-hypernuclear spectroscopy with the (e, e'K+) reaction,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 900, 69–83 (May 2018), DOI: 10.1016/j.nima.2018.05.042 .
- S. N. Nakamura, T. Gogami, L. Tang for the JLab Hypernuclear Collaboration, “Spectroscopic study of Λ hypernuclei with electron beams at Jefferson Lab,” JPS Conf. Proc. 17, 011002-1–13 (2017), DOI: 10.7566/JPSCP.17.011002 .
- T. Gogami, … ,Y. Fujii, … , M. Kaneta, S. Nagao, S. N. Nakamura et al. (HKS (JLab E05-115) Collaboration), “Spectroscopy of the neutron-rich hypernucleus 7ΛHe from electron scattering,” Phys. Rev. C 94, 021302(R)-1–6 (August 2016) DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevC.94.021302 .
- T. Gogami, … , Y. Fujii, … , M. Kaneta, S. Nagao, S. N. Nakamura et al. (HKS (JLab E05-115) Collaboration), “High resolution spectroscopic study of 10ΛBe,” Phys. Rev. C 93, 034314-1–7 (March 2016), DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevC.93.034314 .
- A. Esser, S. Nagao, … , Y. Fujii, T. Gogami, … , M. Kaneta, … , S. N. Nakamura et al. (A1 Collaboration), “Observation of 4ΛH hyperhydrogen by decay-pion spectroscopy in electron scattering,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 232501-1–5 (June 2016), DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.232501 .