| Program C01 | Novel and interdisciplinary application of hard X-ray and gamma-ray detectors |
|---|---|
| Principal Investigator | TAKAHASHI, Tadayuki (The University of Tokyo) |
We aim to advance X-ray and gamma-ray imaging technologies which have
been developed for space observations and apply them to different
research fields, such as in quantum-beam experiments, non-destructive
material analysis, and medical imaging.
Through a series of satellite and rockets experiments, we have
established cutting edge technologies to make highly sensitive hard
X-ray and gamma-ray detectors. In addition to capabilities of
detecting very faint celestial objects in the sky, space observations
require that these detectors be compact and consume power very
efficiently as well as having to withstand the extreme environment
of space itself once the detectors are in orbit. It has become clear
that this technology can advance knowledge in other to fields of
research. Adapting this technology to other fields is expected to
further increase hard X-ray and gamma ray sensitivity in future space
missions than are presently available.
In-vivo and three-dimensional gamma-ray imaging of small animals,
such as mice and rats, plays a key role in the study of drugs and
drug-delivery systems in order to invent new methods of medical
diagnosis and treatment of cancer in the pre-clinical phase. One of
our focus at Kavli-IPMU is to advance our present prototypes of 3D
SPECT system, which is based on a high resolution CdTe imager. This
prototype 3D SPECT system aims to shed light into the hidden
processes that cancer studies wish to illuminate.
Multi-probe in vivo imaging of rodents with high spatial resolution
using SPECT has yet to be establish because of the low energy
resolution of current SPECT systems. In small animals, the
accumulation of radioisotope is low and the size of the target in the
body is very small, compared with human bodies. The gamma-ray imagers
should have high detection sensitivity and should also provide high
spatial resolution. The CdTe imaging detector with its multi-pinhole
optics, which was developed by our group, has at present a spatial
resolution of a few 100 μm and it is projected that the imager will
reach a spatial resolution better than 100 μm in the near
future. Furthermore, its excellent energy resolution of 1-2 keV
(FWHM) can detect low-energy gamma-rays and can also provide
simultaneous imaging of multiple radioactive molecules and
discriminate between different radiopharmaceuticals which emit
gamma-rays of different energies.
Since RI (Radio Isotope)-probes are important tools of cancer
research, activities should include the designing of novel chemical
compounds for use in biological experiments, synthesizing
radioisotope-labeled drugs, biological analyses using cells and small
animals, and the development of drug delivery systems for
theranostics. Achieving these goals will require a multi
interdisciplinary approach and this is what we have organized for the
C01 research team.
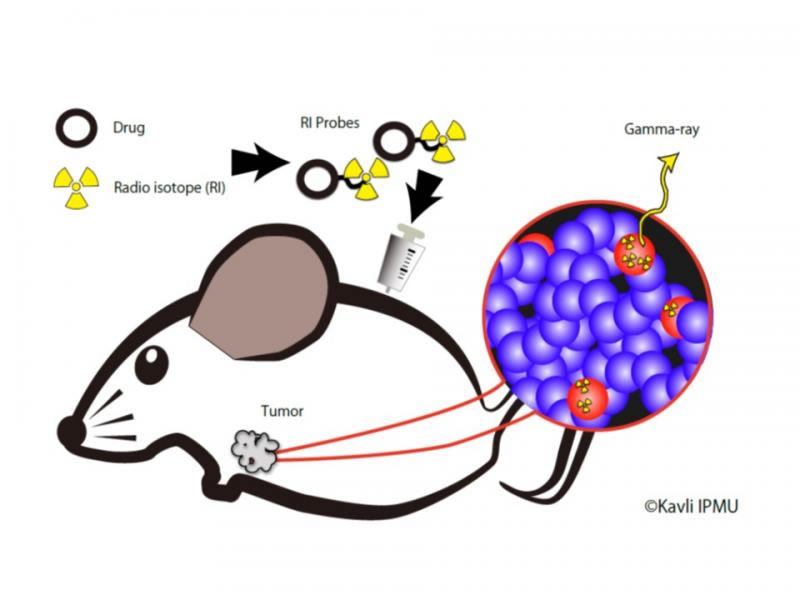 Conceptual diagram of imaging technology developed by the
program C01 for detection of cancer stem cells.
We observe the increase/decrease of cancer stem cells in vivo
(shown in red), by visualizing their distribution.
To achieve this, we will develop a high-resolution
3D imaging system based on space gamma-ray detector technology, and a
radioactive probe (RI Probe) that can selectively accumulate in the
target cancer stem cells.
Conceptual diagram of imaging technology developed by the
program C01 for detection of cancer stem cells.
We observe the increase/decrease of cancer stem cells in vivo
(shown in red), by visualizing their distribution.
To achieve this, we will develop a high-resolution
3D imaging system based on space gamma-ray detector technology, and a
radioactive probe (RI Probe) that can selectively accumulate in the
target cancer stem cells.
Members
| Principal Investigator | TAKAHASHI, Tadayuki (Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe, the University of Tokyo (Kavli IPMU)) |  |
|---|---|---|
| Co-Investigators | TAKEDA, Shin'ichiro (University of Tokyo (Kavli IPMU)) | |
| ORITA, Tadashi (University of Tokyo (Kavli IPMU)) | ||
| YAGISHITA, Atsushi (University of Tokyo (Kavli IPMU)) | ||
| NOMACHI, Masaharu (Osaka University) | ||
| UCHIYAMA, Yasunobu (Rikkyo University) | ||
| OLTEA, Sampetrean (Keio Univesity) | ||
| MASUKO, Takashi (Kinki University) | ||
| Research Collaborators | WATANABE, Shin (JAXA) | |
| IKEDA, Hirokazu (JAXA) | ||
| CARADONNA, Pietro (University of Tokyo (Kavli IPMU)) | ||
| UMEDA, Izumi O. (University of Tokyo (Kavli IPMU)) | ||
| KATSURAGAWA, Miho (University of Tokyo (Kavli IPMU)) | ||
| SAYA, Hideyuki (Keio Univesity) | ||
| NAKANO, Takashi (Gunma Univesiry) | ||
| NINOMIYA, Kazuhiko (Osaka University) |
Reference Materials
- S. Takeda, M. Katsuragawa, T. Orita, … , S. Watanabe, T. Takahashi … , “A high-resolution CdTe imaging detector with multi-pinhole optics for in-vivo molecular imaging,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A, in press (2017), DOI: 10.1016/j.nima.2017.10.037 .
- M. Katsuragawa, M. Tampo, … ,Y. Miyake, … , T. Takahashi, S. Takeda, S. Watanabe et al., “A compact imaging system with a CdTe double-sided strip detector for non-destructive analysis using negative muonic X-rays,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A, in press (2017), DOI: 10.1016/j.nima.2017.11.004 .
- A. Yagishita, … , H. Saya et al., “Development of highly selective fluorescent probe enabling flow-cytometric isolation of ALDH3A1-positive viable cells,” Bioconjug. Chem. 28, 302–306 (2017), DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00618 .
- H. Nobusue, … , H. Saya et al., “Regulation of MKL1 via actin cytoskeleton dynamics drives adipocyte differentiation,” Nat. Commun. 5, 3368 (2014), DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4368 .
- T. Takahashi, S. Watanabe, … , S. Takeda, “High-resolution CdTe detectors and their application to gamma-ray imaging,” Biological and Medical Sensor Technologies, Ed. K. Iniewski, CRC Press, 339–366 (2012), ISBN: 9781138073210 .

