| Program C02 | Advanced negative muon beam development |
|---|---|
| Principal Investigator | MIYAKE, Yasuhiro (High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK)) |
Research Objective:
The C02 group aims at developing an ultra-low speed negative muon
beam that can be focused at a nanoscale level, and by scanning the
converged negative muon beam create a scanning negative muon
microscope, which could non-destructively visualize isotopic element
and chemical bond distributions three-dimensionally with extreme high
sensitivity, and becomes a revolutionary analytical microscopic
tool. When a negative muon is captured by an atom in a material, it
releases characteristic muonic X-rays with nearly 100% probability,
and because their energies are 200 times higher than electronic
X-rays, they are easy to detect. Light elements such as hydrogen and
lithium, as well as carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen, which are
the main elements in living organisms, can easily be detected with
high sensitivity. For example, by observing while scraping the
surface of a rapidly frozen biological sample, it will be possible to
comprehensively reconstruct three-dimensional distributions of
elements, isotopes and chemical bonds constituting a living body with
nanoscale resolution capability, thus providing a new analytical tool
to revolutionize biological fields.
Research Goal:
Formation of a negative muon beam that can be focused into a diameter
of
Step 1: few tenth of a millimeter,
Step 2: a few micrometers,
Step 3: several tens of nanometers.
Research Plan:
The research plan will be performed in two stages: (1) advanced
negative muon, and (2) ultra-low speed negative muon beam
development.
(1) Improvements of the Negative Muon Beamline at J-PARC
Improvements of the negative muon beamline at the J-PARC muon
experimental facility, which is the foundation of this research
project and has already achieved the world's highest intensity pulsed
muon beam, will be carried out by online beam monitoring and
automatic beam tuning program to obtain a well-focused muon beam at
the sample position. Thus, establishing the research environment
necessary to promote negative muon research focused on A01, B01 and
B02 groups. In FY2018, by introducing a collimator that allows
measurement in the air and an advanced beam monitor to realize
narrow-momentum muon beam, the experimental environment will be
improved for B01 group of non-destructive analysis and C01 group of
high-resolution photodetector.
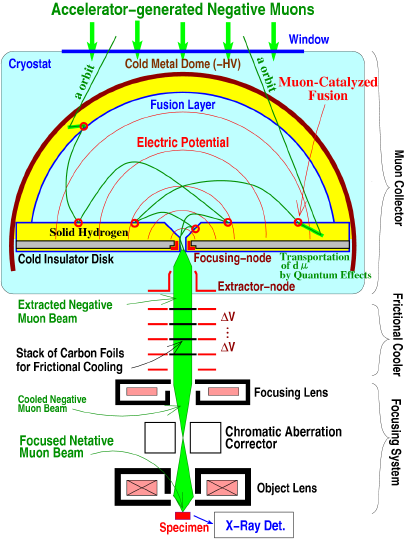
(2) Developments of Ultra-Low Speed Negative Muon Beam
Although the negative muon beam obtained in (1) has high-intensity,
it is difficult to focus. Utilizing muon catalyzed fusion reaction as
a beam cooling means, ultra-low speed negative muon beam that can be
converged up to nanoscale diameter will be developed. Negative muon
beam with "high-spatial coherence (= small emittance)" can be focused
to a smaller beam size. Therefore, by cooling high-energy negative
muons to about several keV by muon catalyzed fusion reaction, and
reaccelerating them, the beam can then be converged by using a
chromatic aberration correction optical system. Furthermore, by
developing an energy dispersion correction device, negative muon beam
with "time coherence" in energy and momentum will be realized. Then a
scanning negative muon microscope will be developed with
high-brightness and excellent temporal and spatial coherence to
perform three-dimensional elemental analysis experiments. Ultimately,
realizing the world's first ultra-low speed negative muon beam and
scanning negative muon microscope.
Members
| Principal Investigator | MIYAKE, Yasuhiro (Institute of Materials Structure Science, High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK-IMSS)) |
 |
|---|---|---|
| Co-Investigators | NAGATANI, Yukinori (KEK-IMSS) | |
| STRASSER, Patrick (KEK-IMSS) | ||
| Research Collaborators | SHIMOMURA, Koichiro (KEK-IMSS) | |
| KAWAMURA, Naritoshi (KEK-IMSS) | ||
| YAMAZAKI, Takayuki (KEK-IMSS) | ||
| TAKESHITA, Soshi (KEK-IMSS) | ||
| TAMPO, Motonobu (KEK-IMSS) | ||
| ISHIDA, Katsuhiko (RIKEN) | ||
| UMEGAKI, Izumi (KEK-IMSS) | ||
| NINOMIYA, Kazuhiko (Osaka University) | ||
| UENO, Hideki (RIKEN) | ||
| NOMACHI, Masaharu (Osaka University) |
Reference Materials
- Y. Miyake, K. Shimomura, N. Kawamura, … , P. Strasser, … , S. Takeshita, … , M. Tampo et al., “J-PARC muon facility, MUSE,” JPS Conf. Proc. 21, 011054-1–6 (2018), DOI: 10.7566/JPSCP.21.011054 .
- M. Katsuragawa, M. Tampo, … ,Y. Miyake, … , T. Takahashi, S. Takeda, S. Watanabe et al., “A compact imaging system with a CdTe double-sided strip detector for non-destructive analysis using negative muonic X-rays,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A, in press (2017), DOI: 10.1016/j.nima.2017.11.004 .
- P. Strasser, … , Y. Miyake et al., “The Development of a Non-Destructive Analysis System with Negative Muon Beam for Industrial Devices at J-PARC MUSE,” M. Tampo, … , N. Kawamura, … , K. Ninomiya, JPS Conf. Proc. 8, 036016-1–6 (Sep. 2015), DOI: 10.7566/JPSCP.8.036016 .
- H. Okamoto, Y. Nagatani “Entanglement-assisted electron microscopy based on a flux qubit,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 062604-1–4 (Feb. 2014), DOI: 10.1063/1.4865244 .
- K. Terada, K. Ninomiya, … , Y. Miyake, … , N. Kawamura et al., “A new X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy for extraterrestrial materials using a muon beam,” Sci. Rep. 4, 1–6 (May 2014), DOI: 10.1038/srep05072 .