| Program C02-1 | Development of a flat-top RF acceleration cavity for negative muon microbeam production |
|---|---|
| Principal Investigator | YAMAZAKI, Takayuki (KEK-IMSS) |
This research aims to develop a novel RF cavity for a flat-top
acceleration system, which is a key device to produce a negative muon
microbeam. A negative muon microbeam will enable us to scan a sample
with a high position resolution. In addition, non-destructive 3D scan
could be realized if beam energy is scanned. The improvement of the
brilliance of a negative muon beam is an important milestone for
muon colliders as well.
As a source of a negative muon microbeam, we use negative muons
produced by pion decays. These muons have large momentum dispersion,
therefore it is impossible to focus them due to chromatic
aberration. To reduce the momentum dispersion, first these muons are
cooled via muon catalyzed fusion (μCF) and frictional cooling as
proposed by the C02 group. After the cooling process, the energy of
negative muons is about 10 keV with 100 eV dispersion. Though the
dispersion is still large for microbeam production, the C02 group
plans to use an aberration collector which consists of several
lenses. On the other hand, this research assumes to use
re-acceleration of cooled muons up to E = 1–10 MeV by a
flat-top RF cyclotron, in order to reduce ΔE/E
down to less than 10–4 and avoid
chromatic aberration.
A flat-top acceleration is a well-established technique and used in
heavy ion cyclotrons (see references), but the short lifetime of
muons (2.2 μs) makes it difficult to develop its RF cavities. The RF
frequency of the muon acceleration system should be about 10 times
higher than conventional cyclotrons, therefore we have to develop a
new type of a flat-top acceleration cavity for a muon cyclotron.
In this research, the flat-top RF cavity adopts not a conventional
λ/4 coaxial resonator, but a λ/2 coaxial resonator, but a
center-shorted λ/2 coaxial resonator. This design is based on an
open patent (No. 2002-43097), but this type of cavity has not ever
been developed and fabricated actually.
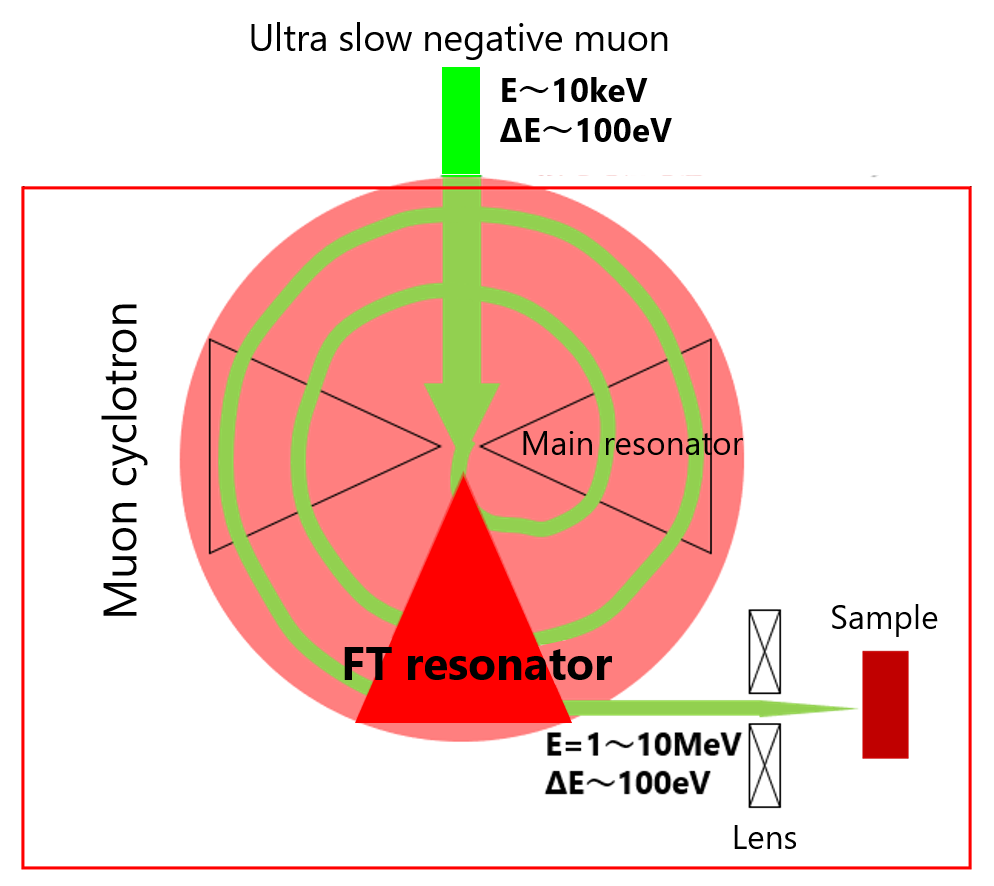 In this research, we consider a cyclotron equipped with a
flat-top acceleration system, as a reacceleration method for
producing a ultra-slow negative muon micro beam. We will
develop a new flat-top resonator, which is the most important
device to be developed to realize this cyclotron.
In this research, we consider a cyclotron equipped with a
flat-top acceleration system, as a reacceleration method for
producing a ultra-slow negative muon micro beam. We will
develop a new flat-top resonator, which is the most important
device to be developed to realize this cyclotron.
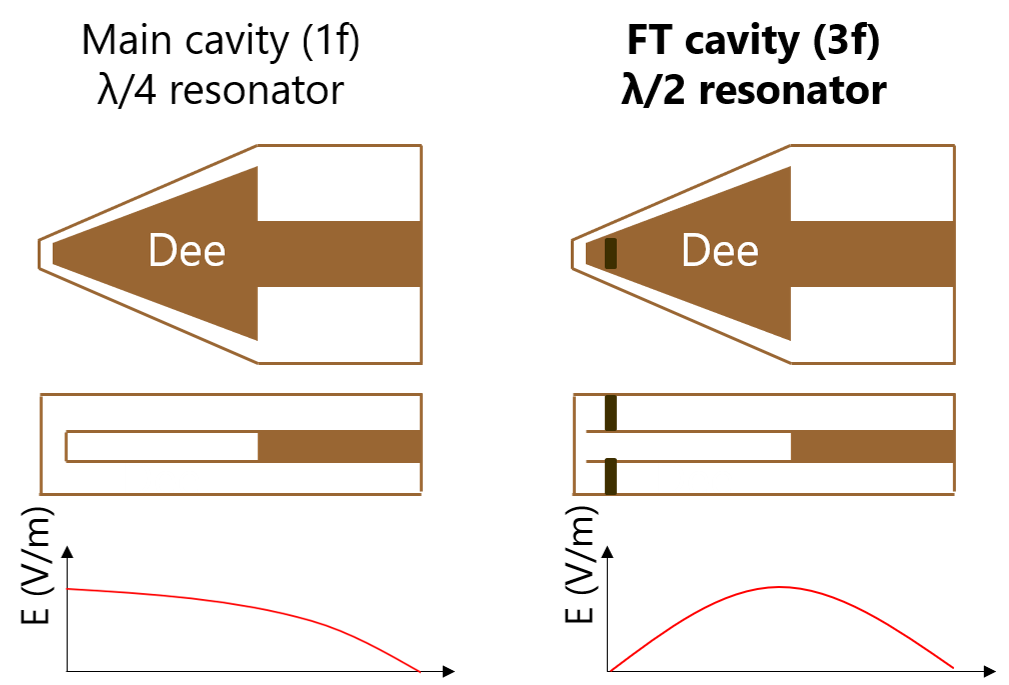 The flat top cavity developed in this research is a
λ/2 resonator (right) by shorting the central
region, unlike the usual λ/4 resonator (left) used in
conventional cyclotrons. The design of the resonator is
based on the patent of Sumitomo Heavy Industries, Ltd., Yukio
Kumada (Patent Number 2002-43097), and this is the first research
to actually carry out detailed design and production.
The flat top cavity developed in this research is a
λ/2 resonator (right) by shorting the central
region, unlike the usual λ/4 resonator (left) used in
conventional cyclotrons. The design of the resonator is
based on the patent of Sumitomo Heavy Industries, Ltd., Yukio
Kumada (Patent Number 2002-43097), and this is the first research
to actually carry out detailed design and production.
Members
- Principal Investigator
-
YAMAZAKI, Takayuki
(KEK-IMSS)
- Research Collaborators
Reference Materials
- S. Kurashima et al., “Improvement in beam quality of the JAEA AVF cyclotron for focusing heavy-ion beams with energies of hundreds of MeV,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 260, 65 (2007).
- M. Oikawa et al., “Focusing high-energy heavy ion microbeam system at the JAEA AVF cyclotron,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 260 85 (2007).
- W. Yokota et al., “Development of Microbeam Formation and Single-ion Hit Technologies at the TIARA Cyclotron,” JAEA-Technology 2014-018.
